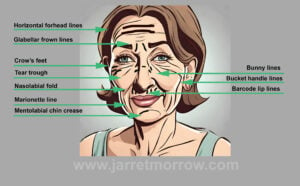
Jarret Morrow MD is a cosmetic physician located in Edmonton. Other than Botox®, Dysport® and dermal fillers (Restylane® and Juvederm®) or IPL laser, here are seven more tips to look younger than your age. Today we’re going to review anti-aging skin care tips from a recently published article in the Journal, Maedica.
Tips to Look Younger?
Desmond Morris, a renowned zoologist, said it best when he stated, “flawless skin is the most desired human feature.” Morris’s statement could not be any closer to the truth. It is human instinct to present their best selves. Good looking skin is a representation of well-being, health, and fertility. With an increase in life expectancy, healthy aging strategies are being taken to prevent mental and physical ailments.
The skin, an extremely important organ, affects the general health of humans in a profound manner. It is a barrier against the environment and also helps to control our immunity. Its appearance affects social interactions, self-esteem, social interactions, and our quality of life. The skin is affected by extrinsic and intrinsic factors. Intrinsically, the skin functions begin to naturally decline with age. In extrinsic aging, environmental factors such as pollution, UV exposure, diet, stress, and smoking have adverse effects on the appearance of the skin. Even though aging cannot be avoided, no one wants to be perceived as looking old for their age.
An individual who is said to look older than they are is normally seen as being in poor health. Perceived age has been used as a method to predict mortality for years. Perceived age can be associated with several genetic factors as well as socioeconomic status, depression, body mass index, smoking, and sun exposure. Pigmented spots, wrinkles, sun damage, skin texture, and the color of the skin are all associated with the age that a person is perceived to be. Wrinkles and pigmentation changes can make a person appear older than they are. Studies have shown that color distribution and wrinkles can account for a twenty-year difference in an individual’s perceived age.
Vital Factors Involved in Aging Skin
There are two processes that affect the way that the skin ages are intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic factors are affected by time, while extrinsic reasons are caused by environmental factors. Intrinsic aging, the natural skin aging process, is an aging process that cannot be controlled. Extrinsic aging occurs as a result of the environment and its elements. Certain lifestyle choices such as smoking, drinking, and diet, are considered extrinsic aging factors. An individual’s facial expressions and sleeping positions are also considered to be environmental factors associated with aging.
The face undergoes various transformations as it ages. Age affects the shape of the face, its texture, and the color of it. The signs of aging skin can be classified into four categories. These four categories include wrinkles, decreased firmness, pigmentation abnormalities, and vascular conditions.

1. How the Sun Affects Perceived Age
Western culture has promoted tan skin as an attractive and healthy attribute to encompass. Due to this “beauty standard”, there has been an increase in skin disorders and neoplasms. Skin cancer has increased and the aging process of the skin has accelerated.
Two influential twentieth-century dermatologists, Dubreuilh and Unna, recognized the adverse effects that increased sun exposure had on the face. They performed their research by comparing the faces of outside workers to those of inside workers. Nearly seventy years later, Albert Kligman released his findings regarding sun exposure.
Photoaging
Kligman found that those who were exposed to the sun forced their skin to undergo various structural changes. In 1986, Kligman introduced a new term to the industry. The created term “photoaging” is used to differentiate extrinsic and intrinsic aging factors. Photoaging takes into account the normal aging process and damage that occurs to the tissues as a result of repeated sun exposure.
Minor exposure to the sun causes modification to DNA, sunburn, and immune system suppression. However, long-term exposure can cause premature skin aging and certain types of skin cancers. Long term sun exposure causes changes in the color and texture of the skin and as a result, the skin loses its natural translucency and becomes rough with deep creases and folds.
Photoaging has a profound effect on chronological skin aging. Several researchers have estimated that eighty percent of facial aging is due to photoaging; others will argue that this number is closer to ninety percent. Changes in the skin’s pigment are one of the most visible effects of photoaging.

2. How Sugar Affects Skin Aging
An intriguing article published in 1945, highlighted the link between sugar levels in the skin and serum. Sugar levels in the skin decrease whenever a low sugar diet is followed. Foods that are high on the glycemic index and refined carbohydrates cause insulin levels to spike, which is then followed by inflammation.
The link between skin health and diet has been researched for several years. When elastic fibers and collagen change, this results in the skin sagging and its elasticity depleting. Diet, specifically, a diet that is high in sugar can accelerate the obvious signs of aging. Fructose and glucose, which are introduced into the body by the foods that we consume, increase the production of protein molecules with sugar stuck on them (advanced glycation products) which increase the skins stiffness and decrease its elasticity.
The levels of glucose in the body are connected with the way the skin ages. Increased exposure to sugars is associated with prematurely aging human skin fibroblasts.
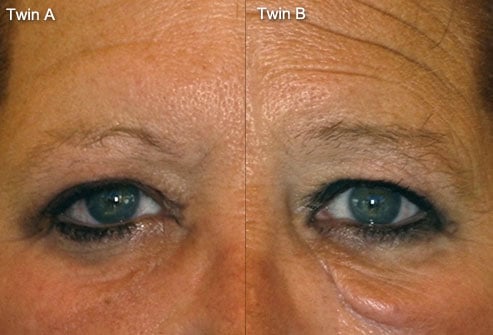
3. How Smoking Influences Skin Aging
Solly, published the first paper that connected smoking with premature skin aging. This paper was published in 1856. According to Solly, smokers skin showed prominent signs of aging such as wrinkles, and a sallow complexion, in comparison to nonsmokers. One hundred years after this first paper, Ippen, reported in 1969 that people who smoke look older than their counterparts who do not smoke.
In 1985, the term smokers face was coined. Smoking is one factor that is associated with skin aging. Wrinkling on the face occurs as a dose-response relationship to performing the act. There are some authors that believe that smoking is a greater contributor to skin wrinkling than exposure to the sun. There are 3800 constituents found in tobacco smoke and the negative effects of this smoke on the skin are apparent on the epidermis and indirectly in the blood circulation of the dermis.
Smokers face is a common term. It involves a squinted eye appearance and pursed lips. Fine lines begin to appear in this area, mimicking the appearance of the face when cigarettes are smoked. The vascular structures of the skin are constricted by short-term and long-term smoking. Smoking deprives the skin’s tissues of nutrients. The effects of smoking on the skin are similar to those of chronic exposure to UV rays.

4. How Skin Care Affects Skin Aging
Environmental factors or extrinsic aging is responsible for eighty percent of the visible signs of aging skin. These outside factors include sun exposure, smoking, diet, pollution, and daily skin care habits. Skincare routines were first mentioned in 1883. The FDA defines cosmetics as, “products that are intended to be applied to the human body to cleanse it, beautify it, or promote attractiveness through modifying its appearance”. Basically, cosmetics are intended to protect the skin, while reinforcing its attractiveness and beauty.
A lot of the active ingredients that are compounded to create these cosmetic products are designed to help reduce damage to the skin’s surface while also promoting healthy skin aging. Cosmeceuticals are cosmetic products that are designed to be administered topically to the skin to enhance the health and beauty of the skin. These dual-purpose products fit a niche between cosmetics and drugs. Also, cosmeceuticals can be used for both the skin and hair. Options to stimulate collagen production to improve the skin’s appearance include products such as topical vitamin c, retinols (Vitamin A derivatives), and alpha hydroxy acid (AHA’s).
When it comes to the skin, prevention, protection, cleansing, and moisturizing are the primary components of a proper skin care regimen. Sunscreen should be used daily, because sun damage occurs from everyday exposure, more often than not. A proper skin care routine can slow down the skin aging process (more).

5. How Stress Affects Skin Aging
Stress is a harmful stimulus that has negative effects on the body, and the skin. The duration of the stressful event along with the individual’s reaction to it can cause various body defense mechanisms to react. Immune dysfunction, DNA damage, and oxidative stress are some of the most accepted aging principles and stress is involved in all of them.

6. How Sleep Affects Skin Aging
The body requires rest so it can repair itself from the outside stressors that it faces daily. Poor sleep quality is associated with poor self-assessments and facial appearance. Sleep is connected with attractiveness. People who are sleep deprived appear fatigued, and not as attractive as their rested counterparts. Obvious signs of sleep deprivation include reduced skin elasticity, fine lines, uneven skin pigments (more).

7. Seconds (Time / Age).
With the advances in science that have been made, life expectancy has increased. People have access to more money and choose to spend their time outdoors engaging in leisurely activities. Even though being outdoors is great, there are long-term effects that the skin shows over time. These effects come in the form of saggy, wrinkled, and uneven skin pigmentation. While we can’t stop the clock completely, there are common cosmetic procedures including Botox and dermal fillers that can slow the clock down.
To book a free consultation with Dr. Morrow click here to contact Dr. Morrow.
Reference:
- Clatici V.G., Racoceanu D., Dalle C. Voicu C., Tomas-Aragones L., Marron S.E., Wollina U., Fica S. Perceived Age and Lifestyle. The Specific Contributions of Seven Factors Involved in Health and Beauty. Maedica 2017 12(3), 191-201