One of the common refrains from patients are concerns about their botox wearing off too quickly–It’s an understandable concern as treatments are expensive. What if there’s a way to prolong the effect of Botox? Let’s find out…
Botox, or botulinum toxin type A, is a leading aesthetic treatment for reducing dynamic wrinkles, typically requiring maintenance injections every three to four months. Some patients report early fading of effects, while others claim prolonged results with zinc supplementation. This article examines the scientific evidence behind zinc’s potential to extend Botox’s effects, focusing on its role in both cosmetic and neurological applications.
How Does Botox Work?
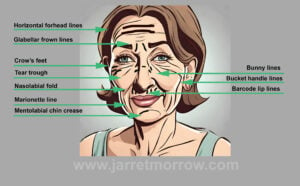
Botulinum toxin type A temporarily paralyzes targeted facial muscles to reduce dynamic wrinkles. It blocks acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contractions, by binding to nerve endings, internalizing, and cleaving the SNAP-25 protein. This process relies on zinc as a critical cofactor in the toxin’s enzymatic activity.
The Role of Zinc in Botox’s Mechanism
Zinc is an essential mineral involved in numerous enzymatic reactions, including the zinc-dependent metalloprotease enzyme in botulinum toxin. This enzyme requires zinc to cleave SNAP-25 and inhibit nerve signals. Zinc deficiency may impair this process, prompting research into whether supplementation could enhance Botox’s efficacy or duration.
Key Studies: Zinc and Botox Longevity
A 2012 double-blind, placebo-controlled trial by Koshy et al. investigated whether zinc combined with phytase could extend Botox’s effects. Participants, all habitual Botox users, were randomized into two groups:
- One group received Zytase™, a supplement containing 25 mg of elemental zinc and phytase, an enzyme that enhances zinc absorption by breaking down phytate—a compound in plant-based foods like grains and legumes that inhibits zinc uptake, particularly relevant for vegetarians.
- The other group received a placebo.
Patients taking Zytase™ experienced an average 30% increase in the duration of Botox’s wrinkle-reducing effects compared to their baseline treatments. The placebo group showed no significant change. However, the study authors developed Zytase™, introducing significant potential for financial bias that may have influenced the study’s design, results, or promotion, warranting caution in interpreting the findings.
A 2023 systematic review by Mallat et al. further explored zinc’s role in enhancing botulinum toxin’s effects. Analyzing 260 studies, the review retained three randomized controlled trials and one case report. Three of these studies found that zinc supplementation significantly improved the effect and longevity of botulinum toxin in both neurological conditions (e.g., dystonia) and cosmetic uses. The review suggests zinc supplementation could be a valuable strategy but calls for larger clinical trials with objective measurement tools to confirm its role.
Why Zinc Might Help: Biological Plausibility
Several factors support zinc’s potential to enhance Botox’s effects:
- Enzymatic Activation: Zinc is essential for the botulinum toxin enzyme to cleave SNAP-25, blocking neurotransmitter release. Deficiency may reduce efficacy.
- Zinc Deficiency Prevalence: Suboptimal zinc levels are common, particularly among vegetarians (due to high phytate intake), older adults (due to reduced absorption), and individuals with malabsorption disorders like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease.
- Enhanced Toxin Efficiency: Supplemental zinc may optimize the toxin’s enzymatic activity, leading to more effective and prolonged neuromuscular blockade.
However, zinc cannot indefinitely extend Botox’s effects. Nerve endings regenerate, and the body metabolizes the toxin over time. Zinc may improve initial injection efficiency but does not alter the toxin’s fundamental pharmacology.
Clinical Practice and Anecdotal Reports
Despite limited scientific evidence, many aesthetic and neurological practitioners recommend zinc supplementation for patients with inconsistent or short-lived Botox results. A common protocol involves taking zinc 4 days before and 3–4 days after treatment, especially for:
- Clients with fast metabolism or high muscle mass.
- Individuals with low-zinc diets (e.g., vegetarians).
- Patients with variable treatment durations.
- Those with chronic stress or malabsorption disorders that deplete zinc levels.
Is Zinc Safe? Dosage Considerations
The National Institutes of Health sets the tolerable upper intake level for adults at 40 mg of elemental zinc per day. The Zytase™ supplement, containing 25 mg of elemental zinc, is below this limit and safe for short-term use in healthy adults. The Mallat et al. review supports short-term zinc supplementation as low-risk, but long-term or high-dose use may cause side effects, such as copper deficiency or immune suppression.
Should You Take Zinc Before Botox?
Evidence suggests short-term zinc supplementation may be a low-risk strategy to potentially enhance Botox’s longevity in cosmetic and neurological applications. Consider these guidelines:
- Consult Your Provider: Your injector or physician can assess if zinc supplementation is suitable, especially if you have risk factors for zinc deficiency.
- Start 4 Days Before Treatment: This aligns with the Koshy et al. study protocol.
- Avoid Long-Term High Doses: Excessive zinc can lead to adverse effects.
- Consider Zinc with Phytase: Products like Zytase™ may improve absorption, especially for those with high-phytate diets.
Limitations and Need for Further Research
The evidence has notable limitations:
- The Koshy et al. study was small and has not been replicated.
- The authors’ financial interest in Zytase™ raises significant concerns about bias.
- It remains unclear whether zinc alone, without phytase, provides similar benefits.
- The Mallat et al. review highlights promising results but emphasizes the need for larger clinical trials with objective measurement tools to confirm zinc’s role in maximizing botulinum toxin effects.
Conclusion
A biologically plausible rationale, supported by a preliminary study and a systematic review, suggests that zinc supplementation may enhance the longevity of botulinum toxin’s effects in cosmetic and neurological applications by optimizing its zinc-dependent enzymatic activity. This approach appears promising for patients with rapid Botox metabolism, inconsistent results, or risk factors for zinc deficiency, such as vegetarian diets or malabsorption disorders. However, zinc should be used cautiously under medical guidance due to potential risks of overuse. Until larger, independent studies confirm these findings, zinc supplementation remains an evidence-informed, but not fully evidence-based, strategy. Patients should consult a qualified practitioner to evaluate its potential benefits and risks.
References
- Koshy JC, Sharabi SE, Feldman EM, Hollier LH Jr, Patrinely JR, Soparkar CN. Effect of dietary zinc and phytase supplementation on botulinum toxin treatments. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11(4):507-512. PMID: 22453589.
- Montecucco C, Schiavo G. Structure and function of tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins. Q Rev Biophys. 1995;28(4):423-472. doi:10.1017/S0033583500003292. PMID: 8771234.
- Wessells KR, Brown KH. Estimating the global prevalence of zinc deficiency: results based on zinc availability in national food supplies and the prevalence of stunting. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50568. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050568. PMID: 23209782.
- Mallat F, Kaikati J, Kechichian E. Botulinum toxins and zinc: from theory to practice—a systematic review. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2023;46(4):141-145. doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000557. PMID: 37335837.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) Office of Dietary Supplements. Zinc Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/. Accessed June 7, 2025.